Understanding Data Visualization Techniques
Written on
Chapter 1: The Importance of Data Understanding
In the realm of Data Science, grasping the essence of a dataset is paramount. Without a clear understanding of what a dataset represents or the characteristics it contains, deriving valuable insights becomes nearly impossible. To effectively analyze data, a variety of techniques can be employed, ranging from statistical analysis to the creation of visual graphs. Each method plays a crucial role and reveals different facets of the information, allowing for diverse interpretations. In this article, we will explore five distinct chart types that can significantly aid in data comprehension.
Section 1.1: Distribution Plot
A distribution plot, often referred to as a distplot, serves as a powerful tool for visualizing data. This type of graph illustrates how data points are distributed across the entire dataset, whether focusing on a single feature or the dataset as a whole. The distribution might resemble a normal distribution—centered around a mean of zero with a standard deviation of one—or it may appear skewed, either to the left or right. Below is an example of a distribution plot.
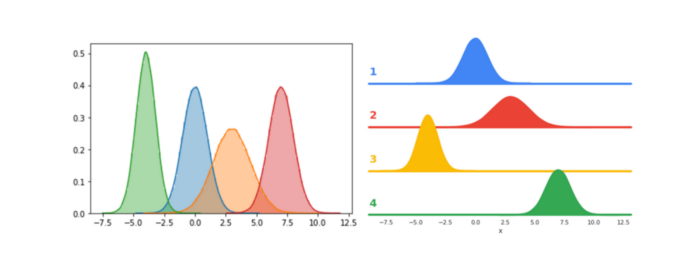
Section 1.2: Pie Chart
Most individuals are familiar with pie charts, yet these simple visualizations can convey critical information that enhances data interpretation. A pie chart allows us to visually assess how a specific feature varies across the distinct categories present within the data. For instance, if we wish to analyze the population distribution across different areas of a city, a pie chart can effectively present these proportions. Additionally, we can emphasize certain categories by isolating them in the chart, often referred to as "exploding" the pie. Below is a graphical representation of a pie chart.
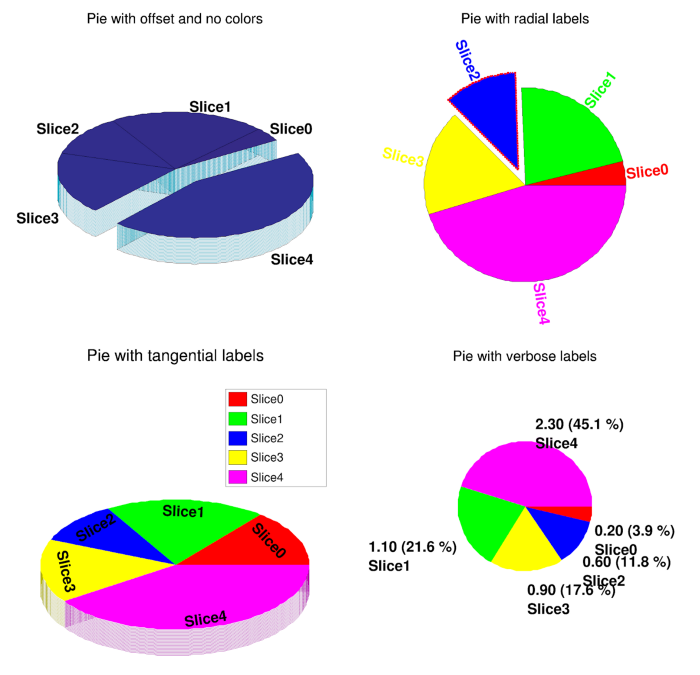
Section 1.3: Line Plot
Line plots are particularly useful when examining data trends over time, allowing us to visualize how a specific feature behaves throughout different periods. For example, analyzing sales data via a line plot can reveal patterns, such as increased sales during weekends or holidays. These visualizations provide valuable insights into temporal data behavior. Below is an illustration of a line plot.
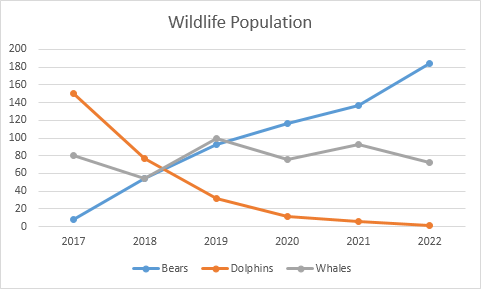
Section 1.4: Scatter Plot
Similar to line plots, scatter plots are effective for analyzing relationships between variables. They provide a visual representation of how two features are related or distributed within the dataset. Understanding these relationships—whether direct or indirect—helps us comprehend the nature of the data. Below is an example of a scatter plot.
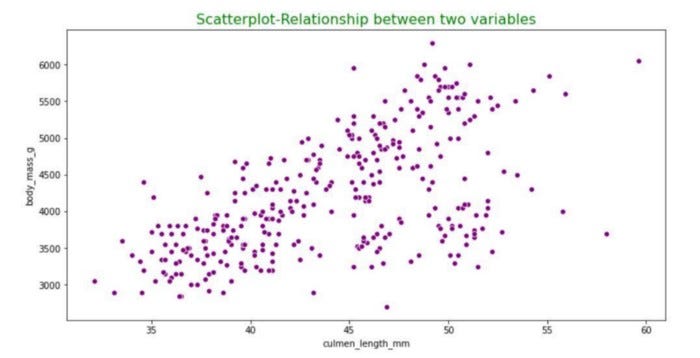
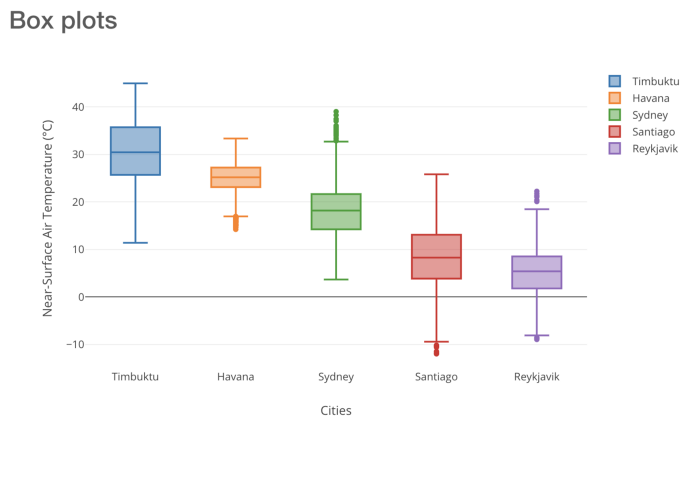
Section 1.5: Box Plot
The box plot is another valuable visualization tool, particularly when we want to summarize statistical information about a dataset. It allows us to identify the median, maximum, and minimum values of a particular feature category. For instance, if we're interested in the sales of various watch types across different categories, a box plot can provide insights into median sales, maximum and minimum sales figures, and even highlight outliers. Below is an example of a box plot.
Chapter 2: Video Resources for Data Understanding
The first video, "Intro to Understanding Data," provides a foundational overview of data comprehension techniques, including various visualization methods.
The second video, "Understanding Data Types and Structures | Google Data Analytics Certificate," delves into different data types and their structures, further enhancing your understanding of data analysis.